The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) refers to the branch of the Federal Reserve System (FRS) that determines monetary policy in the United States by directing Open Market Operations (OMOS). The FOMC meeting is a key event in the financial markets and is considered one of the most important events in the economic calendar.
Also, the Federal Open Market Committee meeting is very important for Forex market traders because, in these meetings, the Federal Reserve (the central bank of the United States) announces its decision on interest rates. This report has a significant impact on the price of the US dollar and can cause many fluctuations in the market.
In this article, we have introduced the members of the FOMC, the time of the FOMC committee meetings, the duties of the FOMC committee, and examples of its performance.
Also Read: Retrace Forex Trading – An Ideal Trading Strategy For Beginners
Contents
- How Does the Federal Reserve Work?
- What is the FOMC?
- Duties of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
- Members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
- The Current Composition of the Board
- Domestic Positions in the Federal Reserve Bank
- Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) Meetings
- Conclusion
- FAQ

How Does the Federal Reserve Work?
Reserve System has three main components:
1. Board of Governors
The seven members of the Board of Governors directed the entire Fed system. They guide monetary policy and set discount rates for member banks, and staff economists provide all analyses.
2. Twelve regional banks
Overseeing the country's commercial banks and implementing policies, 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks cooperate with the Board of Directors.

3. Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
This committee supervises the operation of the open market.
What is the FOMC?
The FOMC is an important part of the Federal Reserve that deals with monetary policy. In December 1913, the Federal Reserve System was created by President Woodrow Wilson and the United States Congress to serve as the central bank of the United States. Purpose The Federal Reserve aims to achieve stable prices while at the same time working to increase and optimize the employment situation.

The FOMC sets policy based on the economic outlook by changing short-term interest rates. Also, since 2009, the FOMC has used large-scale bond purchases (known as quantitative easing “QE”) by lowering long-term interest rates to improve economic conditions and provide fiscal relief.
Duties of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
The Federal Reserve controls three monetary policy instruments: liquidity ratio to reserves, the discount rate, and open market operations. These tools allow the Federal Reserve to control the supply and demand of the amounts held at the central bank by depository institutions and affect interest rates. The FOMC's decision on interest rates has a significant impact on other economic variables, including exchange rates, short-term interest rates, prices of services and goods, and even employment.
The Federal Reserve has the instruments to supply increment or diminish the cash. This is finished through OMOs, discount rate guidelines, and required bank saves. The Federal Reserve Board of Governors is responsible for setting the discount rate and holding prerequisites, while the FOMC is explicitly liable for OMOs, which require buying and selling government securities.

Securities purchased by the FOMC are deposited into the Federal Reserve System's Open Market Account (SOMA), which consists of a domestic and foreign pool. The domestic portfolio includes US Treasury and Federal agency securities, while the foreign portfolio includes investments in the euro and Japanese yen.
Under the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 and the Monetary Control Act of 1980, the FOMC can hold these bonds until maturity or sell them at its discretion. A percentage of the Federal Reserve's SOMA assets are held in each of the 12 domestic banks. However, the New York Fed conducts all of the Fed's open market transactions.
Also Read: What Is The Fibonacci Circle?
Members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
The committee consists of seven board members, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four other members who rotate from the heads of other state central banks. The 12 members of the FOMC meet eight times a year to decide on possible changes in short-term monetary policy. A vote to change the policy results in buying or selling US government securities in the open market to boost the national economy.
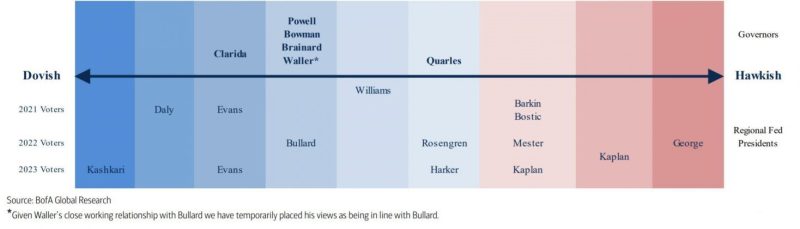
The President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York holds the position of Vice Chairman of the FOMC. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York is the only permanent chairman of the FOMC. The other four chairmen serve on a rotating basis for one year in a three-year program. Each year, the Federal Reserve Board of Directors is elected from the following geographic groups:
- Richmond, Boston, and Philadelphia
- Chicago and Cleveland
- Dallas, Atlanta, and St. Louis
- Kansas City, San Francisco, and Minneapolis
This system ensures that all regions of the United States are represented on the FOMC.
The Current Composition of the Board
The current composition of the board is as follows:
- Committee Chairman Jerome Powell was sworn in for a second four-year term on May 23, 2022. He was first elected as Speaker in February 2018 and belonged to the moderate faction.
- The FOMC Vice Chairman is Lael Brainard. He was sworn in for a full four-year term on May 23, 2022, and joined the board in June 2016.
Other members of the Federal Reserve Board include Michelle Bowman, Lisa Cook, Philip Jefferson, and Christopher Waller.
Domestic Positions in the Federal Reserve Bank
There are 12 domestic positions in the Federal Reserve, each with its own Federal Reserve Bank. These domestic banks act as a branch of the central bank. The president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York is a permanent member of the FOMC, and the heads of other banks serve one-year terms on a three-year rotation schedule.
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) Meetings
The FOMC has eight regular meetings yearly but can hold more meetings if needed. These meetings are not held publicly, so there is much speculation on Wall Street as analysts try to predict whether the Fed will increase or decrease the money supply, as the amount of money supply affects interest rates.
In recent years, FOMC committee minutes have been released to the public after the meetings. In these meetings, members discuss the developments of the domestic and global financial markets as well as economic and financial forecasts. All members share their views on the country's economic position and discuss monetary policies that will benefit the country the most. After much deliberation, only appointed members of the FOMC can participate in the appropriate policy vote for that period.
Conclusion
FOMC is an important part of the Federal Reserve that deals with monetary policy. The FOMC makes policy based on the economic outlook by changing short-term interest rates. The FOMC's interest rate decisions depend on other economic variables. Among other things, the exchange rate, short-term interest rate, price of services and goods, and even employment have a significant effect.
The committee consists of seven board members, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four other members who rotate from the heads of other state central banks. The 12 members of the FOMC meet eight times a year to decide on possible changes in short-term monetary policy.
FAQ
Who Is the Chairman of the Federal Reserve?
The Chairman of the Federal Reserve sets the direction of the Board of Governors and the FOMC. Current Fed Chairman Jerome Powell, a board member, began his term on February 5, 2018.
What Is the Federal Reserve System Like?
The Federal Reserve System has three main components: the Board of Governors, 12 regional banks, and the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
What Is the FOMC?
FOMC is an important part of the Federal Reserve that deals with monetary policy. The FOMC makes policy based on the economic outlook by changing short-term interest rates.
What Are the Duties of the FOMC?
The FOMC's decision on interest rates has a significant impact on other economic variables, including exchange rates, short-term interest rates, prices of services and goods, and even employment.
Who Are the Members of the FOMC?
The committee consists of seven board members, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four other members who rotate from the heads of other state central banks.
When Are the FOMC Meetings Held?
The 12 members of the FOMC meet eight times a year to decide on possible changes in short-term monetary policy.