As a professional trader with extensive experience in the forex markets, I can attest that an FX forward is an essential tool for hedging against exchange rate risk. This financial instrument involves an agreement between two parties to exchange a specific amount of one currency for another at a predetermined rate on a future date.
By locking in an exchange rate today for a transaction that will occur in the future, businesses and investors can protect themselves from adverse currency fluctuations that might otherwise impact their financial stability. This is particularly crucial for companies engaged in international trade or investment, as even minor changes in exchange rates can significantly affect profitability.
The Use of FX Forwards
The strategic use of FX forwards allows firms to budget and forecast with greater accuracy, knowing that their future foreign currency needs are secured at a known rate. This mitigates the unpredictability associated with fluctuating currency markets, ensuring that companies can focus on their core operations without the added stress of potential currency risk.
Additionally, investors looking to protect their portfolios from volatile exchange rates utilize these forward contracts to stabilize returns. By leveraging FX forwards, both companies and investors can achieve greater financial certainty and operational efficiency, highlighting the importance of this instrument in effective risk management strategies.
Also Read: How To Maneuver Exchange Rates
Mechanics of FX Forward Contracts
In an FX forward contract, the two parties agree to exchange currencies at a future date, known as the delivery date. The exchange rate, referred to as the forward price, is established at the time the contract is agreed upon. This forward price is calculated by adjusting the current spot price according to the interest rate differentials between the two currencies involved. This adjustment ensures that the forward price accurately reflects the cost of carrying the currencies until the delivery date, accounting for the differing interest rates in the respective countries.
I emphasize the importance of understanding these mechanics when engaging in FX forwards. The difference between the spot rate and the forward price represents the anticipated change in value due to these interest rate differentials, which is a critical factor in determining the true cost and benefit of the contract. This detailed knowledge allows traders and financial professionals to make informed decisions, ensuring that the use of FX forward contracts aligns with their risk management and financial objectives.
Hedging Currency Risk with FX Forwards
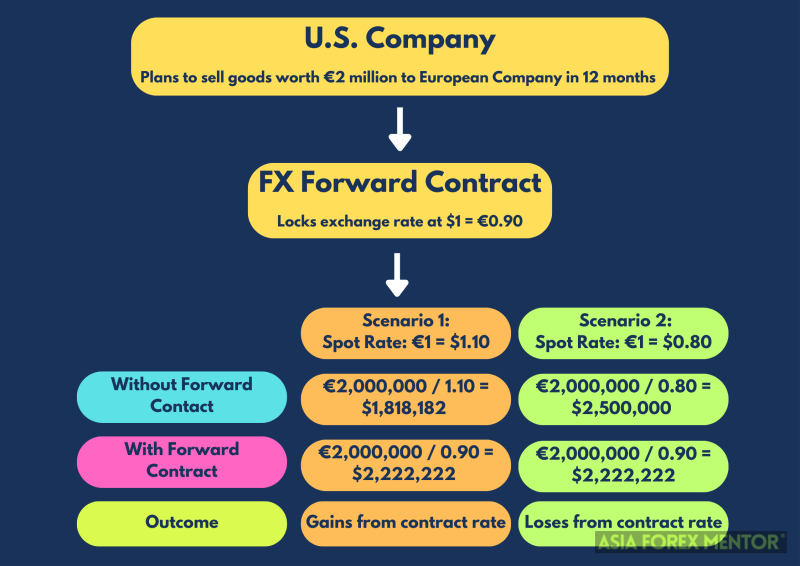
Companies and investors utilize FX forwards to hedge against currency risk, a vital strategy in safeguarding their financial interests. For instance, a US-based company anticipating a payment in euros six months from now can enter into a forward contract to sell euros and buy US dollars at a predetermined rate. By locking in this rate, the company ensures that it knows the exact amount it will receive in dollars, regardless of any fluctuations in exchange rates over the six months. This level of certainty is crucial for accurate budgeting and financial planning, as it removes the unpredictability associated with volatile currency markets.
I can attest that this hedging strategy provides businesses with the stability needed to focus on their core operations without the distraction of potential financial losses due to adverse exchange rate movements. Moreover, investors can also benefit from FX forwards by stabilizing returns on international investments, thereby enhancing their overall portfolio management. By mitigating the risks associated with currency fluctuations, companies and investors can achieve more reliable financial outcomes, ultimately supporting long-term growth and stability.
How Does FX Forwards Work?
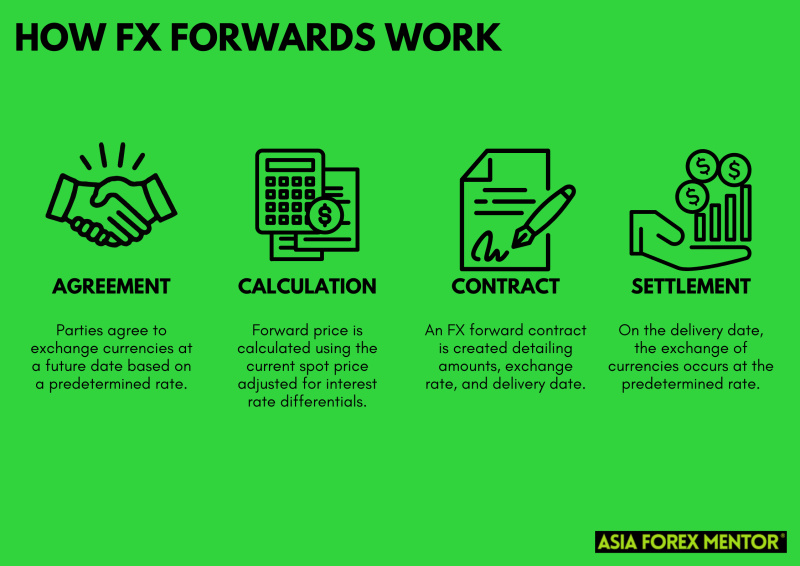
When trading FX forwards, the process involves several meticulous steps to ensure both parties are protected from unwanted currency fluctuations.
- Agreement: The initial step involves both parties—typically a business and a financial institution or two corporations—agreeing to exchange a specified amount of one currency for another at a future date. This agreement is based on a predetermined exchange rate, which is established at the outset. This agreement is essential as it sets the terms and conditions, including the currencies involved, the amounts, and the future date for the transaction.
- Calculation: The next step is the calculation of the forward price. This price is not arbitrarily set but is derived from the current spot price of the currencies involved, adjusted for the interest rate differentials between the two currencies. The interest rate differential reflects the difference in interest rates between the two countries. By factoring in these differentials, the forward price ensures that the cost of carrying the currencies until the delivery date is accurately represented. This calculation is crucial for ensuring that the contract remains fair and reflective of market conditions.
- Contract: Once the forward price is determined, an FX forward contract is created. This legally binding document details all aspects of the agreement, including the amounts of the currencies to be exchanged, the exact exchange rate, and the specified delivery date. The contract serves as a formalized agreement that both parties will adhere to the terms set forth, providing legal protection and clarity. This step ensures that there is no ambiguity about the transaction details, which is vital for both operational efficiency and financial planning.
- Settlement: The final step is the settlement of the contract. On the agreed-upon delivery date, the actual exchange of currencies takes place at the predetermined forward rate. This means that regardless of the current spot price on the delivery date, the exchange occurs at the rate agreed upon in the contract. This settlement process ensures that both parties fulfill their obligations, providing the certainty and stability required for effective risk management. This certainty allows businesses to manage their finances with a clear understanding of their future currency exchanges, aiding in precise financial forecasting and budgeting.
Benefits of FX Forwards

- Hedging Exchange Rate Risk: FX forwards protect against adverse movements in exchange rates, providing financial certainty.
- Flexibility: They can be tailored to match the specific needs of the parties involved, including the amount, currencies, and delivery date.
- No Initial Costs: Generally, there are no upfront costs associated with entering an FX forward, unlike options contracts that may require a premium.
Risks and Considerations
While FX forwards offer significant benefits, there are also risks:
- Credit Risk: The possibility that one party may default on the contract.
- Market Risk: Unfavorable changes in interest rate differentials can affect the forward price.
- Liquidity Risk: Some currency pairs may have lower liquidity, affecting the ease of entering and exiting contracts.
Conclusion
FX forwards are a powerful tool for managing exchange rate risk in international transactions. By locking in a specific rate for future currency exchanges, businesses and investors can ensure financial stability and predictability. However, it's crucial to understand the associated risks and work with reputable financial institutions to manage those risks effectively.
Also Read: What Is Spot Trading?
FAQs
What is the main advantage of using FX forwards?
The primary advantage of using FX forwards is the ability to hedge against exchange rate risk. By locking in an exchange rate for a future transaction, companies and investors can protect themselves from adverse currency fluctuations. This ensures financial stability and predictability, which is crucial for budgeting, financial planning, and safeguarding profits in international transactions.
How is the forward price in an FX forward contract determined?
The forward price in an FX forward contract is determined by adjusting the current spot price of the currencies involved by the interest rate differentials between the two currencies. This calculation takes into account the cost of carrying the currencies until the delivery date, ensuring that the forward price reflects the true market value and the differing interest rates in the respective countries.
Are there any risks associated with FX forwards?
Yes, while FX forwards offer significant benefits, there are also risks involved. The primary risks include credit risk, where one party may default on the contract, and market risk, where unfavorable changes in interest rate differentials can affect the forward price. Additionally, there is liquidity risk, especially with less commonly traded currency pairs, which can make entering or exiting contracts more challenging. It's essential for parties to fully understand these risks and to work with reputable financial institutions to mitigate them effectively.