The global financial crisis in 2008 created many turbulent situations for some of the largest companies, especially in the car manufacturing industry. One such example was the Volkswagen short squeeze.

This was not a prolonged event, it occurred over 4 days, and resulted in a decline of 58%, forcing hedge funds to mobilize in an attempt to recover from the undermining situation.
For a better perspective, this case from over 13 years ago is very similar to what happened with GameStop. And historically there are other events that more or less follow the same pattern. But the 2008 VW short squeeze is a good case example.
We are going to explore the example and draw a few conclusions that can be useful not to get trapped in that situation.
Also Read: How to Trade the Squeeze Momentum Indicator
Contents
- What Is Short Selling?
- Short Selling Example
- Short Squeeze Meaning
- Defining the Short Interest Ratio
- Characteristics of a High Short Interest Stock
- The VW Short Squeeze
- VW Short Squeeze Timeline
- The Fallout of the VW Short Squeeze
- How Long Did the 2008 VW Short Squeeze Last?
- Porsche Won In The Volkswagen Short Squeeze of 2008
- Similarity to GameStop
- The Biggest Short Squeeze In History
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Is Short Selling?
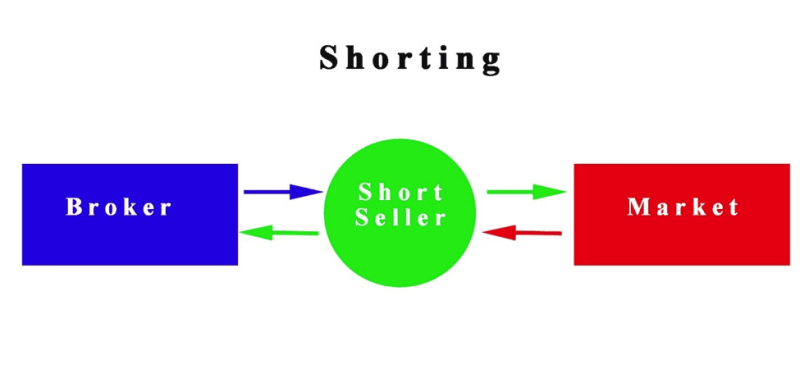
Short selling is a trading strategy, implemented by investors that bet on a future decline in the price of a specific stock.
In most cases, investors do not own the asset they are trading. Usually, traders borrow a specific quantity of shares they plan to sell during a higher market price and repurchase the stock after a decline. Earning a return from the price difference between the two.
This is not without risk, because the borrowed stock has to get returned, and the price may not go down, but rise, creating a situation where the investors will lose money on the trade.
Investors that use this type of trading strategy get referred to as short-sellers.
Short Selling Example
To get a better idea about how short selling functions, we will inspect an example.
A trader is following the market and thinks the airline industry is facing a slump after oil prices rise, and some companies are having trouble filling seats.
The investor selects a company that in his assessment will continue to decline in the short term.
The trader decides to act on his belief and make an order to short sell 100 shares of the target company and gets filled $10.
The broker loans the shares and sells them in the trader’s name. The investor’s balance rises to $1,000, and the shares worth declines to $1,000. At this point, the trader owes the broker 100 shares.
If the bet pans out and the stock price starts to decline, at this point the investor can purchase 100 shares at a lower price and return them to the broker.
This process gets referred to as short-covering, and the price difference between the original selling and the following repurchasing of the stock is the profit.
If the prediction does not come true and things move in the other direction, then the trades will have to purchase the share at a higher price and incur a loss.
Short Squeeze Meaning
A short squeeze is an opposite situation of what traders were originally planning and starts when the stock price begins to rise drastically rapidly, creating pressure on short-sellers that wagered counter the stock to work fast and purchase the stock back in an attempt to stay clear of further losses.
This is a problem in itself because when short-sellers begin purchasing back their short positions, they activate a loop.
Their activity in the market is interpreted by other investors as more interest in the stock, and this new demand attracts traders which raises the price even higher. This results in more short-sellers covering their positions.
This is happening very often on a small and large scale, and one such example occurred in 2021 with GameStop, whose stock rise abruptly when retail investors began purchasing the stock.
Investors that expected GameStop to decline were surprised by the new interest and found themselves in a short squeeze. They had two choices start buying back the stock until the price is still reasonable or stand and face bigger losses.
Defining the Short Interest Ratio
It will not surprise you to learn that there is no consensus on how to calculate the short-interest ratio. Traders frequently clash on the definition because there’s more than one way to calculate it.
This is not alleviated by the fact that various definitions of short interest ratio get circulated.
It’s possible, to begin with, the amount of days needed to cover the short interest as a percentage, and there is the NYSE short interest ratio.
What traders can be sure about is that the interest percentage of 20% is very high.
Additionally, if the day to cover is over 10 this is a sign of serious pessimism. Because of this, the high short-interest stock must be viewed with caution.
Also Read: Total Expense Ratio: Ultimate Guide
Characteristics of a High Short Interest Stock
The core principle remains identical, no matter which definition gets applied, because of this stocks with a high short interest ratio possess a couple of defining elements.
These principles are obvious when looking at the VW short squeeze. When the trend gets sustained in that case traders will be able to learn what to search for.
With a significant quantity of shares sold short or a reduced amount of shares offered for trade. Remembering this if an unexpected purchasing fever is to happen, you will spot short-sellers desperately attempting to cover positions so they can reduce losses.
The VW Short Squeeze
The recession in 2008 was bad news for everybody, but short-sellers of Volkswagen were up for a very unpleasant surprise when a company decided on market manipulation.
This is a good case study because it shows that speculation can occur from other sides, not just from institutions and big money.
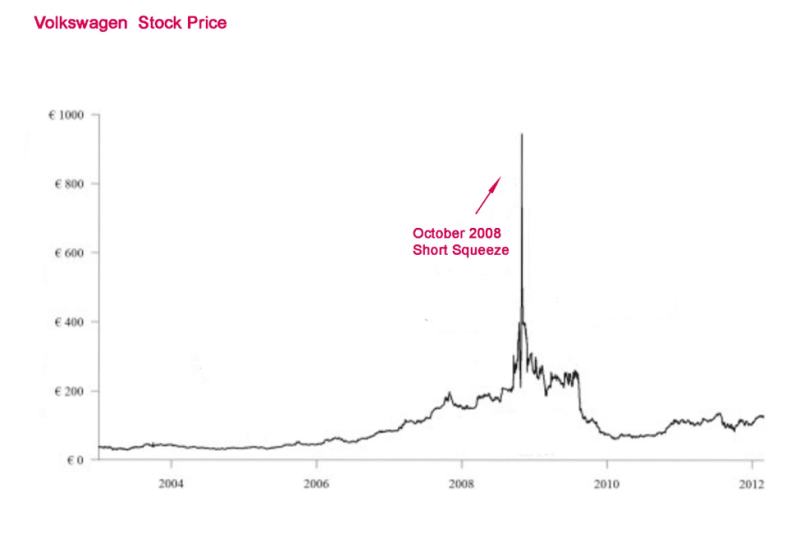
It all happened in an instant, a true shock for traders, that experienced the dramatic rise of German car manufacturer Volkswagen, whose shares quadrupled in a couple of days. This made VW for a short period the most valuable company in the world.
VW Short Squeeze Timeline
This situation has not been a spur-of-the-moment thing, the background can get traced two years earlier when Porsche announced they will be increasing their stake in VW.
This was done the old fashion way by investing in Volkswagen stock. Naturally, the price of the stock price started to go up in the following two years.
Short sellers believed this is the perfect opportunity for their favorite strategy. Experience reveals that overvalued stock typically goes down to its normal level once the hype surrounding the company calms down.
Meaning so-called short-sellers begin doing what they do best shorting the stock.
But the short positions ballooned in 2008. The problem is simple Porsche had 43% of VW shares, plus 32% in options, and the government had invested 20.2%.
There was no maneuvering space for other investors.
Said simply, the actual float declined from 45% of outstanding shares to one percent of outstanding shares. And the relatively low short interest created a big imbalance in supply and demand.
Forcing short sellers to get their hands on millions of shares, but the trading volume was not there, nobody was selling the shares.
The Fallout of the VW Short Squeeze
Porsche expanded on its surprise announcement with exploitation that they didn’t foresee the number of short positions in the market.
The statement produced the expected effect. Causing hysteria among traders that had short shares of VW. Making things worse the announcement came on Sunday, limiting options for short sellers on a day when the market is closed.
This forced short sellers to purchase more stocks, in turn, it caused VW’s stock prices to rise to exacerbate the problem for traders.
By purchasing more stock to cover positions, shot sellers were driving the price up. VW stock price continued to grow through October 2008, creating losses for hedge funds in the billions, but Porsche made a profit.
How Long Did the 2008 VW Short Squeeze Last?
As a rule short squeezes are not prolonged events. In the case of VW the typical pattern developed with shares declining and in a month it was down 70% from the previous October’s peak.
The pattern is standard there is a fast price rise, which is followed by a drastic decline, When the squeeze occurs there is a mad dash from everyone to sell simultaneously.
The entire price is short-term and culminates with the price going back to where it started. Most hedge funds are aware of this dynamic and don’t panic but keep positions and ride the storm.
Traders that have the nerves and capacity to stay the course will get rewarded when the stock declines soon.
Porsche Won In The Volkswagen Short Squeeze of 2008

In the financial world 2008 gets remembered as the worst crisis in a century, but thing were not bad for everybody, Porsche for one emerged victory from the short squeeze at the expanse of short sellers.
The strategy that was implemented by Porsche generated profit for the company worth $10 billion in profit in few weeks.
This was not a random event, Porsche was in need of funds and the best way to fill the bank account was by manipulating the market value Volkswagen’s stock.
It should be known that other market players, many hedge funds that were swept by the mass panic lose somewhere around $30 billion.
Similarity to GameStop

Traders got a reminder that short squeezes are a reality, when in January 2021 video game retailer GameStop, so a price spike of 400% in a single day. All through posts on the online forum Reddit.
This was a coordinated attack on big money by pushing prices up because of large interest. Things settle down in short term with GameStop stock getting back to the normal level within a week.
The Biggest Short Squeeze In History
In the history of the financial world, you can find many cases of a short squeeze, yet the Porsche move was something of epic proportions, that made Volkswagen the biggest company in the automotive industry, and the most valuable in the world.
For a brief moment, supply and demand went out of control, and the share price went higher.
Retail traders were justifiable in panicking, they were not experienced but the reaction of hedge funds surprised many, considering they should have been aware the price will return to the normal level.
Conclusion
When an investor or a hedge fund estimates that shares of a certain company are overvalued, they can decide to short the stock. The problem for the short seller is that he doesn’t own the shares but is borrowing them from a broker.
The idea is to sell them when the price is higher, and repurchase them when the price goes down. And profit from the difference.
However, in the Volkswagen case, the stock did not decline and the disparity caused short sellers to purchase shares so they can redeem their contract.
The estimations are that the VW short squeeze resulted in losses of tens of billions. This was the largest short squeeze in the history of the financial world.
FAQs
How high did VW stock go during the squeeze?
Short sellers that were attempting to close their positions had to pay €1,005 per share. This resulted in the most valued voting stock of a company at that time in the world.
What is the Volkswagen Squeeze?
The Volkswagen short squeeze occurred during the global financial crisis in 2008 after Porsche announced plans to increase shareholdings in VW. This drove the share price higher.
How much did VW short squeeze?
The estimations of VW’s short squeeze show a loss of $38 billion.
What is the largest short squeeze in history?
The biggest historical short squeeze occurred in 2008 with Volkswagen stock.
</h2″the-biggest-short-squeeze-in-history”>



