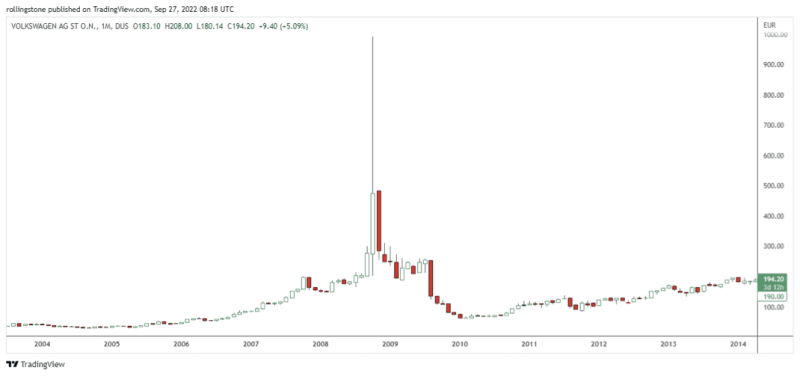
Frankfurt-based Volkswagen shares on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange climbed almost 16% in just one day and became the largest carmaker ever. Following its October 28, 2008 high, the stock plunged 58% in four days, and in Sept, the stock fell 60% to its high, giving off most of the squeeze.
Even after more than a decade since Volkswagen's recent short squeeze, the lesson is still relevant today for the day traders who follow these particular market trends. Let us examine the terms “Short Selling” and “Short Squeeze” and then dive into the 2008 Volkswagen short squeeze.
Also Read: What Was the VW Stock Squeeze
Contents
- Volkswagen – The Company overview
- Why Volkswagen's short squeeze happened and how it unfolded
- What is a short squeeze?
- How long did the 2008 VW Short Squeeze last?
- What is short selling?
- Who are the short sellers?
- Can a Volkswagen short squeeze happen again?
- Short selling examples
- VW Short squeeze schedule
- How long did the Volkswagen short squeeze last?
- What happened in the Volkswagen short squeeze?
- How high did Volkswagen go in the short squeeze?
- Volkswagen stock predictions: Analyst sentiments
- FAQs
Volkswagen – The Company overview
Volkswagen started in the 1930s to provide a comfortable automobile for Germany's middle class. Although wars interrupted efforts to achieve its objectives, the business remained open after 1945, when the occupation ended and resumed operation.

In fact, VW is the third largest car manufacturer in the world, with sales exceeding €200 billion and nearly nine million vehicle sales per year.
Volkswagen owns some of the most coveted cars around the world. Approximately 200 production units will be in operation by November 2021. Volkswagen employs over 300.000 people worldwide.
Why Volkswagen's short squeeze happened and how it unfolded
During the 2008 world financial crash, a strange thing happened. After a brief period, Volkswagen has been briefly made the most valuable company of all time. Back then, Volkswagen became a target for short-sellers because it had incurred huge debt and was heavily exposed to credit and economic cycles.
Several factors were behind Volkswagen's shortfall in revenue. Volkswagen owns large chunks of its shares, with Porsche SE and German authorities holding an equally large share. So a relatively small share could be traded at Frankfurt's stock exchanges.
What is a short squeeze?
A short squeeze refers to unusual activity by short sellers requiring them to buy security to minimize their own risk and increase its value. For short squeezes, the stock must have low short interest, meaning that retail traders have to borrow significant shares to believe their prices would fall.

Short sellers then require buying the asset when it suddenly rises to close the position. The increase in insider trading account volumes increases prices in the securities.
Short squeezes are defined as short-standing trading situations in which traders who have short positions are forced to shut down positions and suffer significant losses due to sudden and outrageous increases in stock price.
The most commonly used word means somebody is destroying the accounts they're holding. However, losses suffered by short-sale are often compared only to loss of purchases, and the difference is between 0 and 0%.
Short squeezes are when stocks start to increase quickly, forcing sellers to purchase them quickly, so they don't have to incur additional losses. When the seller sells a short position, it triggers a loop. Increased supply-demand imbalance attracts buyers and raises prices.
Consequently, short positions must also be covered, or they will be sold. It is impossible to get back to that incredible short squeeze.
Not all shares will perform well in executing short squeeze strategies. Please note that short squeezes are very vulnerable as volatility increases significantly. Here is some investment advice for locating stocks that are suitable for short squeezes:
Most companies have experienced short-cutting, the most recent is GME (NASDAQ: GE) and Tesla (TSLA). We will also examine the famous Volkswagen Short Squeeze in October 2008 in this blog.
How long did the 2008 VW Short Squeeze last?
As you can see, the short squeezes are not lasting. It was not a shock event. In just 4 days, the stock fell 58% & the price dropped 70% from its peaks of 28 October in one month. Lindsey Bell is the senior strategist at Ally Investments.
The price has rapidly increased, and the market is rapidly falling with each short squeeze. Eventually, everyone sells simultaneously. Usually, all squeeze ends the same; Often, the stocks return only to where they had begun the flight. Almost all hedge fund managers know this and stay on top during turbulent times.
Volkswagen's short squeeze of 2008
The origins of the Volkswagen short squeeze of 2008 can be seen in 2006 when Porsche SE started buying a large share in the German automaker. In the months that followed, the price progressively increased as a result.
The 2006 decision by Porsche SE to begin buying a large share in the German automaker is when the history of the Volkswagen short squeeze of 2008 can be found. As a result, throughout the ensuing months, the price increased gradually.
Porsche did not, however, discontinue purchasing VW stock higher than anticipated by market participants. In March of that year, the corporation disclosed that it had increased its holding to over 40% and that it also held around 31.5% of its shares via cash-settled options.
It meant that fewer than 10% of the company's float was truly available and accessible to day traders and investors in the open market reopened when combined with the 20% interest the German government possessed at the time.
What is short selling?
Is there any way of making money if shares drop and then you lose them? Okay, that can be accomplished with a short sale. Let's say you think your company's profits will decrease.
Apparently, whisperings about poor income are whirling. Or maybe the airline has to abandon its flights because the virus has spread worldwide? This may justify the decision to shorten stocks.
When shorting shares, you do not hold them directly and borrow them from your broker. It is like buying something – you have a chance to get it temporarily. Take heed of the VW short squeeze.
Who are the short sellers?
In the financial practice of short selling, an investor, sometimes known as a short-seller, borrows shares and sells them right away in the hopes of later purchasing them (“covering“) at a lower price.
The short-seller makes money if they make more money selling the shares than they lose buying them back because the shares were borrowed and must be finally returned to the lender (plus interest and dividend, if any).
However, a sudden boost in positive news could result in a loss rather than a gain in the stock's share price. Short-sellers might subsequently be compelled to buy the shares they had borrowed at a higher price to prevent their losses from growing should the share price continue to climb.
Short squeezes happen when stock short sellers buy a lot of shares compared to the volume of the market to cover their positions, so-called short sellers. When short sellers buy the stock to cover their short positions, the price of the short stock rises, encouraging additional short sellers to do the same, increasing demand. This dynamic may cause a chain reaction of stock purchases and a further increase in the share price.
Timing of borrowing, purchasing, and selling can cause more than 100% of a company's shares to be sold short. Shorted shares are relisted on the market response and may be borrowed more than once, but this does not always suggest naked short trading.
Stocks with high borrowing costs frequently experience short squeezes. The pressure on sellers to cover their short holdings can rise due to high borrowing costs, further enhancing the reflexive character of this occurrence.
Also Read: What is Short Selling: Profit Making Strategy?
Can a Volkswagen short squeeze happen again?
Volkswagen stock was up nearly 4% during the infamous Meme Stock Short Squeeze in 2021. In the past few days, Volkswagen has had to reduce prices to keep pace with the booming demand for diesel in Europe.
pixabay.com
As of February 18, 2019, VW shares have reached $357.50 a share. Since then, the higher prices have gradually declined and remain reversible since the decline failed during this time and has not climbed above the previous highest level. It's also good practice to consider the differences between VW shares and preferred shares.
Short selling examples
Trade strategies are best explained in the examples below. If you've researched and believe Delta Airlines is reducing its traffic and oil costs are rising, it may continue to lose value, at least through 2020. Frenzy: If one buys stock in DAL for $20, it will take 20 shares to be sold.
Your stockbroker may loan your shares to you for your benefit, if necessary. Your cash balance will increase by $2000, and your share price will fall by $2000. It will now pay the brokerage 100 DAL shares.
VW Short squeeze schedule
Rewind to 2006 as Porsche announced that it wanted to expand its stake in VW. In this regard, Volkswagen had huge investments and purchased VW's shares in boats. Predictably, stock prices have steadily risen in recent months.
Hedge funds watched and saw stock prices overvalue, so they shorted stocks betting on their eventual fall. In late 2009, the short position grew. Porsche's share price jumped by 44% to 31% in option and 20.2% in government ownership.
Many hedge funds and short-sellers speculating on a lower price for shorted VW stock ended were by the revelation. Since the hedge funds had borrowed 13% of the shares of VW and sold them short, Porsche had the upper hand. With only less than 6% of the shares available, this means the hedge funds had to repurchase 13% of the shares.
When a stock rises in price, and short sellers choose to close out their short positions or are compelled to do so by margin calls, the situation known as a short squeeze occurs.
As these short sellers purchase the stock, the price increases, possibly forcing additional shorts to cover. This starts a vicious cycle where the stock rises even higher. In theory, a stock can soar as high as it wants.
How long did the Volkswagen short squeeze last?
The short squeeze of 2008 began on 28 October 2008 when Porsche announced a new stake in Volkswagen. Worse of all, they lasted just days. Soon after Porsche acquired Volkswagen, only 6% of Volkswagen shares were traded against demand from around 12% to cover outstanding short positions.
Porsche released about 5 % of Volkswagen holdings at a stratospheric price, and sellers were able to exit the biggest company. After August 28, stock prices fell 58% within the first 10 hours. In one month, stocks dropped 70%.
What happened in the Volkswagen short squeeze?
The German carmaker suffered an early hit in 2009 when the Porsche company was forced to cut costs. The market was already reeling in the wake of the US bank Lehman Brothers collapse and other financial crises.
The shares in Volkswagen began to grow rapidly as Porsche began to increase its stakes in Volkswagen. The stock continued to grow, even after accumulating a high level of debt and facing financial problems. It was further affected by the 2008 financial crisis and lost sales of its cars.
How high did Volkswagen go in the short squeeze?
Volkswagen shares jumped by 41% over two days, reaching more than 22,000 euros. The sudden rise of the Volkswagen stock market briefly left Volkswagen the most valued company and surpassed ExxonMobil with a market capitalization of about $370 billion.
The financial institutions analyzed the evidence that Volkswagen shares were underinflated and deemed them unsustainable despite their strong valuation. Porsche denied involvement in the stock market manipulation, citing the alleged seller.
Despite ‘extremely weak business' during the 2008 global financial crisis, VW manages to make a profit
Despite the financial crisis, Europe's largest automaker, Volkswagen, posted a first-half net profit of 494 million euros. However, executives cautioned that this year's “very difficult business” would hurt future profitability.
The largest automaker in Europe, Volkswagen of Germany, stated on Thursday that despite the current financial crisis, it was still turning a profit. However, it expressed caution about its prospects.
VW reported a first-half net profit of 494 million euros (695 million dollars), well below expert expectations of roughly 524 million euros and a significant 81 percent lower than the 2.57 billion euros in the same time a year earlier.
Based on the past performance of the last six months, sales decreased 9.4% to 51.2 billion euros. The group supplied 3.1 automobiles in total, a five percent decrease. According to the company, the global financial crisis “seriously damaged” business. Since the end of 2008, the group's cash reserves have increased by 53.1 percent to 12.3 billion euros.
Volkswagen stock predictions: Analyst sentiments
In an interview with Capital.com, Piero Cingari noted that Volkswagen shares had fallen 32% year. It had fallen by 76% to 76% during the previous European recession.
How much did VW stock gain during the 2008 short squeeze?
Between October 24 and August 28, Volkswagen shares have risen by over 50%. On its first day on 28 October.
FAQs
How high did VW stock price go during the squeeze?
Volkswagen's shares were boosted to 517 euros on 27 October 2008 – an increase of almost 45%. The stock price had reached its highest level in the past few days at 9999 euros a share, with short-selling cost estimates ascending to the billions.
How long did VW's short squeeze last?
Has Volkswagen been a victim since 2007, and is this a re-run? It was about 60 percent lower than the highest market cap in its last four days. It took several weeks of re-investment to get back on track.
How much did VW short squeeze?
According to estimates, VW's short squeeze has cost short sellers about 30 to 34 billion US dollars.
Volkswagen's stock rose about 150% between its opening price of €348 and its closing price of €517 on October 27, 2008. The stock reached its all-time high on Tuesday at €999 per share, with short-selling losses pegged at tens of billions of dollars.
Wendelin Wiedeking, the CEO of Porsche, was eventually prosecuted with share price manipulation for his involvement in the short squeeze, but the accusations were later dropped.
What's the biggest short squeeze ever?
In August 2008, VW's falling share price was down from 210.80 to 1.000 on the Xetra DAX in less than two hours, briefly establishing its status as the most valued business on the market.
the shares gained 3.79% against the close of the week of €210.85 share.