

As forex traders develop more long-term trading strategies, they will have to deal with swap fees. Swap fees are the fees that forex traders pay when they carry their position overnight. These fees are also referred to as rollover fees and carry fees.
Swap long and short refers to the paying of swap charges for having a forex rollover in which the trader goes long on one currency and shorts the other currency. The fees can be a credit or debit to the trader’s account, depending on whether the difference between the interest fees on the trader’s currency pair is positive (credit) or negative (debit). For long trades, traders pay interest fees (debits), and for short trades they receive interest payments.
Also Read: What is Swap in Forex?
Contents
- What is Forex Trading?
- What is the Forex Market?
- What is a Forex Swap?
- Profiting from Swap Fees
- 3-Day Swap
- Tom Next Swap
- How to Avoid Swap Fees
- Retail Investor Accounts
- Forex Derivative Trading
- Start Forex Trading
- Key Takeaways
- FAQs
What is Forex Trading?
Foreign exchange trading, also known as forex trading, refers to the buying and selling of different currencies. Retail investors may engage in foreign exchange trading in order to profit from the trade. Institutional investors may also participate in foreign exchange trading to hedge their investments or to guarantee the availability of currency at a specific exchange rate in the future.
To trade forex, you must select the two currencies that you want to use in the trade. The currencies can be major currencies like the U.S. dollar (USD), Canadian dollar (CAD), Japanese Yen (JPY), the Euro (EUR), and the Australian dollar (AUD).
You can also trade more exotic currencies in your foreign exchange trading currency pair. The exotic currencies may not be as readily available on all foreign exchange trading platforms.
What is the Forex Market?
The foreign exchange market is the international market where retail and institutional traders can access and trade currency pairs or enter into derivative contracts that give them the right and/or obligation to to buy or sell a specific currency.
In forex, the first currency listed is called the base currency. The trader goes long on the base. The second currency is called the quote currency. A short position is taken on the quote. The quote is used to buy the base.
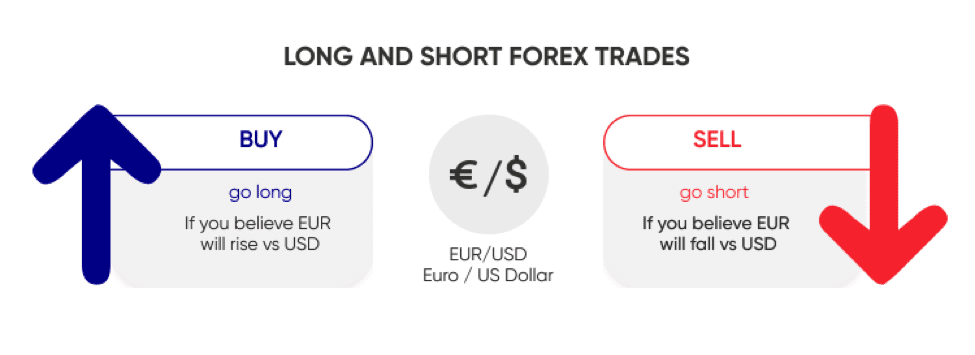
What is a Forex Swap?
When traders keep a forex position open overnight or for more than one night, the trader must pay a carry fee, also known as a rollover fee or swap fee, to the forex brokers. The swap fee is the difference between the interest that must be paid on the long position and the interest received by the trader for holding the short position.
If the difference between the two currencies is positive, the difference will be credited to the trader’s account. However, if the difference between the two currencies is negative, the fee will be debited from the trader’s account.
Currency interest rates are set by the nation that issues the currency. When doing a rollover forex, especially for profit, the trader is advised to consider the interest fees and to try and arrange it so that the net difference between them is positive.
Profiting from Swap Fees
Some traders decide to specialize in swap fees. Their focus is on maximizing the net positive difference between the currency pairs being rolled over to the next trading day.
This strategy is high risk because traders cannot be certain that unforeseen events will not affect the currency values. In short, when the trading day closes you could be in a profitable position, yet the next day be struggling to breakeven or reduce your losses. The trade is even riskier when it’s carried over the weekend.
3-Day Swap
The 3-day swap refers to the delivery of the currency and what happens when the trade is closed after 5:00 pm New York time.
The last day to close a forex trade and not have the closure of the transaction delayed is Wednesday. In forex, after a transaction is closed, it takes 2 days for the currency to be delivered to the trader who purchased it. This is known as the T+2 rule. Although there are some currency trades (e.g., USD/CAD ) that can be settled in one day, T+1, they are not the norm.
If a forex trade is closed after Wednesday, then the transaction cannot be fully settled until Monday the following week. This means that the trader must pay a fee, the net difference between the currency interest rates, for Saturday and Sunday. This is necessary because a forex swap can only be done during the business week, Monday through Friday.
In a retail forex swap, the currency is not delivered to the retail trader. Instead, the forex broker settles the trade for cash, with no physical delivery of the currency. The net difference between the two currencies carried in the trade is debited or credited to the retail trader’s account.
Before doing a 3-day swap, you are advised to look at the interest rates that must be paid for each currency position. Most trading platforms provide this information to you for free. Otherwise, you can research the interest fees for carrying each currency long and short, and then decide which positions you want to keep open overnight.
Tom Next Swap
A tom next swap is a swap that is carried over to the next day. A “tom next” swap is short for “tomorrow next” swap. This occurs when a trader does not close the trade by the end of the trading day, but there is still enough time during the week to settle the forex transaction. So, you can do tom next swaps on Monday, Tuesday and Wednesday. But after Wednesday, your forex trade will be a 3-day swap.
How to Avoid Swap Fees
Retail traders can avoid swap charges if they open and close their trades during the same trading session. This is done in high frequency trading and intraday trading.
Opening and closing trades during the same trading session also reduces trading risks for the trader. The trader does not have to worry about how news or events will affect forex exchange rates and possibly affect the profitability of the forex trade.
Retail Investor Accounts
Retail investors never receive delivery of the physical cash, the cash purchased during the forex trade. It is normal for retail forex trades to be settled in cash for the profits earned and losses incurred during the orex trade.
Let’s look at some aspects of trade forex.
Technical Analysis
Many forex traders use technical analysis to make decisions about their forex trades. They may look for forex indicators in market charts that are short (e.g., 5, 10, 60 minutes) or over longer periods of time (4, 5, 6 hours).
Technical analysis can help traders select the best forex currency pairs for long and short trades of different durations. The currencies must be chosen based on anticipated future performance
Are Swap Charges High?
Beginner traders may be concerned about rollover fees. Unless traders are planning to do a lot of 3-day swaps or make their profits primarily from swap charges, the interest fees charged for keeping the positions open overnight are not important.
Market investments that involve complex financial instruments like options, contract for difference, and other derivatives should be approached with caution by inexperienced investors.
Forex Derivative Trading
The risk involved in trading forex will vary based on the kind of forex swap you do. For example, trades with unlimited losses are higher risk than trades with capped losses or those limited to the initial investment.
Also Read: What Are Trade In Derivatives?
Start Forex Trading

For traders who are not confident about trading in the forex market, they can get forex market news from trading platforms, investment services, or seek independent investment advice from forex brokers. You can also join a platform that provides demo accounts to its users.
Key Takeaways
Forex traders who keep their positions open overnight, or for more than one night, must pay swap fees, also known as carry. The net fee is the difference between the interest paid on the long position and interest received for the short position. If carry is positive, the trader’s account is credited. If negative, it is debited for the money owed. For most traders, carry is insignificant.
Forex traders can set up currency pairs that result in positive carry. They can also choose to focus on profiting from positive carry.
If you want more assistance with setting up forex trades, there are a plethora of resources available to you. You can use the resources on a forex trading platform, observe online forum discussions about forex trading, or work with an independent investment advisor. The resource(s) you use may vary over time and with your budget. Make the best trade decisions for you and your trading future.
FAQs
Do I need a lot of money to become a forex trader?
No, you don’t need a lot of money to become a forex trader. You can open a forex trading account with US$10.
If you are a beginner trader, find trading platforms with demo accounts, no minimum balance (or a really low one), and no account maintenance fees.
Is forex trading difficult?
Like everything else, forex trading will be challenging when you first start doing it. With time, attention to your trading strategies and results, and the drive to become a successful trader, you can improve your forex trading performance.
Note, you may not become rich from it, or even make a lot of money from it, but you can at the very least improve your trading results over time.
How can I become good at forex trading?
According to forex traders, you become good at forex trading by trading forex and learning from your successes and failures. You can also watch YouTube videos, read trading magazines, participate in online forum discussions, and use the resources provided by your trading platform.
Is foreign exchange trading high risk/high reward?
Foreign exchange trading can be high risk/high reward, low risk/low reward, and moderate risk/moderate reward. In general, the higher the risk (the greater the chance of failure), the greater the potential reward.



