Sector Rotation is when investors move some capital from their stock market portfolio to other stock market sectors. This is done by selling your stocks in one industry and using the funds to buy stocks in another sector. Investors tend to capitalize on changes in economic conditions using sector rotation to maximize their earnings.
According to the Global Industry Classification Standard, the stock market can be grouped into 11 different sectors. These sectors are real estate, financial sector, Information technology (ICT), consumer discretionary, energy, materials, consumer staples, health care, industrials, communication services, and utility sector.

Sector rotation can be classified as a type of investment strategy because it involves the management of investment funds. Many investors move their capital to sectors that the economic cycle suggests would have better future performance.
Also Read: Learn How To Make Money with Sector Rotation
Contents
- How Does Sector Rotation Work?
- Economic Cycle that Triggers Sector Rotation
- A Sector Rotation Strategy
- How can Investors Take Advantage of Sector Rotations in the Stock Market?
- Importance of Sector Rotation Strategies
- Conclusion
- FAQs
How Does Sector Rotation Work?
Sector rotation operates by cycling your capital away and into various sectors to benefit from the transitional changes in phases of the economic cycle or changes in the rate of economic growth, from the expansion phase or early cycle phase to the recession phase.
Certain sectors react faster to economic changes when compared to others, rotating capital in and out of these sectors may lead to higher yields or more profits.
Economic Cycle that Triggers Sector Rotation
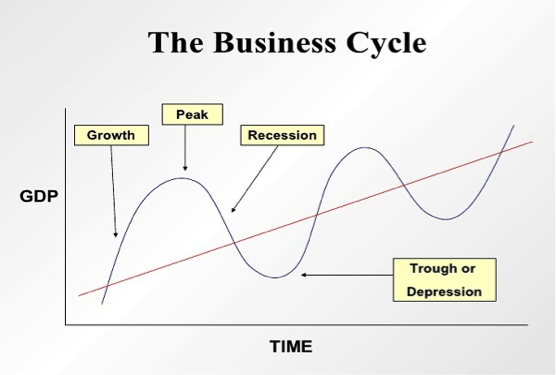
An economic cycle is also known as the business cycle. It indicates changes in activities in an economy. It is sometimes a vital determining factor of equity sector performance over a given period.
All economic cycles are unique and different. Historical performance proves that some patterns and trends in stocks usually reoccur. Oscillations in the stock market cycle are important and they represent an expansion in economic activity.
Unexpected events or announcements can interrupt or disrupt the trend of the stock markets. From past performance, a change in main indicators can help identify the different phases of economic cycles.
There are 4 different phases of a business cycle:
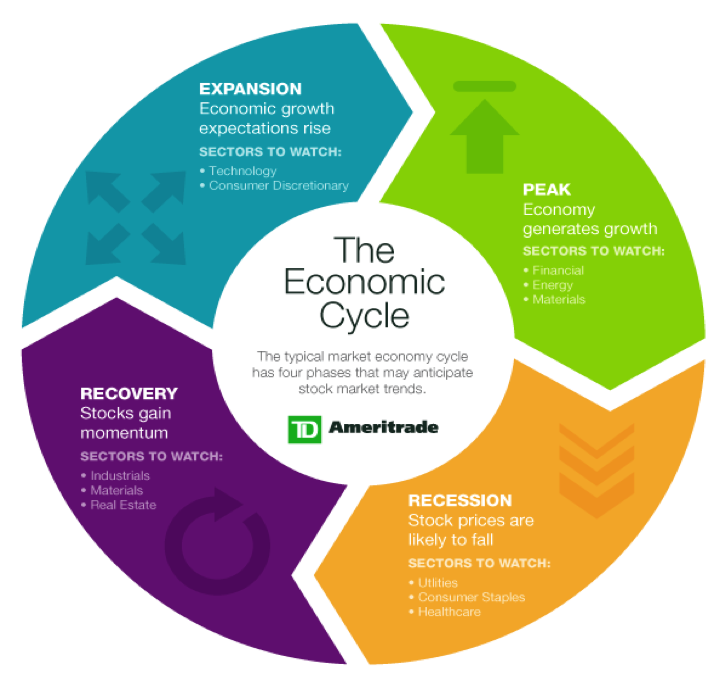
Early cycle phase
This is the recovery phase after the market bottom. This is when the market economy moves from negative growth to positive growth in economic activity. This growth can be measured by increases in Gross domestic product and industrial production.
During this stage, there is high sales volume and low inventory. These are the earlier stages of the business cycle and maybe the beginning of a bull market.
Mid-cycle phase
In this stage, the economy expands. This expanding economy phase is the longest phase of the cycle. Economic weakness goes away as the market gathers momentum and credibility. This is known as the expansion phase.
All monetary policy favors profitability, as the market cycle hits equilibrium. There is economic growth in inventory and sales. There are falling interest rates as the economy grows and creates inflationary pressures.
Late cycle Phase
This is the market top of the business cycle. At this level, inflation is high and the banks are trying to control increasing interest rates. The overall market in the business cycle has hit its peak, and this starts a new trend for the next cycle.
These slow economic growth, low available credits, and declining profit margins. The relative strength of Sales falls as inventory increases exponentially. Stock prices fall as investors take profit.
Recession
This is the final stage of the business cycle. This stage is also known as economic contraction. In the financial market is this stage can be seen as a bear market which could mean a financial crisis.
There are falling sales in this stage, higher interest rates, flat yield curve, and declining industrial activities which could lead to an increase in the unemployment rate.

During this stage of the business cycle, investors rotate their capital into other sectors of the financial markets.
A Sector Rotation Strategy
A sector rotation strategy is a mapped-out plan used by investors to identify when to move their capital to another market sector, and the preferred sector to move to. Sector rotation strategy usually factors in past occurrences, market data, economic research, and business cycles in the same sector.
There are a lot of sector rotation strategies, most strategies are determined by the type of stocks and the sectors. These types of stocks can be classified into cyclical (e.g consumer discretionary) and defensive (e.g. consumer staples).
How can Investors Take Advantage of Sector Rotations in the Stock Market?
Investors would see a business cycle in many sectors of the economy. They may even gain exposure by buying stocks of a particular sector and understanding how that sector operates. Investors who have a good understanding of a business cycle can make better decisions when buying stocks.
With proper knowledge of sector rotation, investors would be able to moderate their portfolio during euphoria. That way they would have more earnings to get a bigger position size for the next cycle.
To take advantage of sector rotation strategies, you can choose to buy either individual stock or ETFs (exchange-traded funds) that aims at various parts of the economy. After, you can adjust your stock portfolio based on your bias or thoughts about a particular sector. Whether they would expand or contract.
If you are looking to go into sector rotation but don’t have sector rotation strategies. You can get managed exchange-traded funds from domestic and foreign markets or mutual funds. Though they may have higher fees, they take away the stress of managing a strategy.
Also Read: Investor Emotions And How It Affects The Stock Market
Importance of Sector Rotation Strategies
Sector rotation can be very straightforward at times and other times complex. Investors can moderate their portfolio amongst two types of stocks. There are cyclical and defensive stocks (non-cyclical)
Cyclical stocks are assets of organizations that are in communication services, information technology, consumer discretionary, and real estate. Cyclical stocks tend to perform similarly poor during a recession.
Non-Cyclical stocks are assets of organizations that have stable stock prices during a recession. These include consumer staples, health care, and utilities.
When the economy is contracting, investors can rotate their investment from Cyclical stocks which might lose value to Defensive or Non-cyclical stocks which are more stable.
A common sector rotation strategy is during the mark-up phases or accumulation phases. Investors rotation into stocks during accumulation and sell their positions after growth, repeating this would bring about good future results.
Conclusion
If you are looking to save your investment from changes in the economy, then you should get some sector rotation strategies. Rotating in and out of sectors based on what’s going on in the economy is a popular technique to follow an active investment strategy.
A rotation may be a reasonably simple technique for the common investor to adopt a more tactical approach to investing and perhaps obtain greater returns by using mutual funds and ETFs.
This method may be utilized in conjunction with whatever portfolio management you’re already performing to ensure you stay within your risk tolerance.
However, not all investors will benefit from sector rotation in specific industries. This is because, unlike a standard buy-and-hold plan, this form of investing strategy necessitates more periodic investment choices. It may also raise your portfolio’s overall uncertainty, as well as increase transaction costs and taxes that you would normally save.
FAQs
How long does sector rotation take?
A recession normally lasts three to four years, while each annual growth cycle usually lasts three to four years. Economic expansion takes a long time to cycle through. The growth phase began in 2008 and lasted 10 years, with the longest cyclical cycles occurring between 1981 and 1982.
How do you rotate funds in the stock market?
You can rotate funds in the stock market by selling the positions you invested in one sector and using the funds to reinvest in other sectors. This way you would rotate your funds amongst various sectors of the economy.
Does sector rotation beat the market?
Sector rotation strategies outperformed the S&P 500 more than half of the time. This goes to show that sector rotation can beat the market and reduce your overall risk if a proper strategy is implemented.
How does the US economy move?
The economy moves in various stages. There are specific periods where the economy contracts and expands, these periods determine how people invest.
When employment, consumer expenditure, and real gross domestic product, or GDP, rise, the economy expands. This is also known as a recovery in the economy.
When business activity slows or real GDP declines, the economy shrinks. The economy may see lower employment and lower consumer expenditure at this point.
The performance of various stock market sectors is influenced by these economic swings. Investors should hold holdings in firms that will outperform the broader market over economic cycles and avoid those that will underperform.






