
In any transaction, one participant carries most of the risk. When you buy fruit, you give the retailer cash and you get the produce. The risk is that you may have gotten spoiled fruit and the vendor’s risk-free money. Risk reversal strategies play a role in any business deal. Eliminating risk is the best way to develop your business. Risk reversal is an options trading strategy used by traders use to prevent losses.
The trading strategy Risk Reversal was created to guard short and long positions. It is a hedging strategy that uses call and put options. Risk reversal is dissimilar from other leveraged speculation because its intention is to accomplish speculation without spare capital outlay. This makes risk a favorite in commodities trading as a mechanism that affirms a certain price without extra cost.
It is also a standard by which you can measure the sentiment of traders. When you are selling for a net debit, this means that call options are more overpriced than put options. This is caused by the volatility of call options .
This insinuates a bullish sentiment on the asset. But when it is selling for a net credit, it means that put options are more costly than call options.
Also Read: Currency Risk
Contents
- Implied Volatility
- When To Use A Risk Reversal
- Risk Reversal Strategy And Underlying Asset
- Risk Reversal And Strike Price
- Application In Stock Price
- Maximum Gain vs Maximum Loss
- Risk Of Early Assignment
- How To Trade A Risk Reversal Strategy?
- Risk Management For Maximum Profit
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Implied Volatility
Volatility also plays a role this time with put options. In this case, we have a Bearish sentiment. In forex trading, risk reversals are based on higher implied volatility. This makes it easy to measure the investor’s sentiment.
These strategies are preferred by institutional investors. Retail traders are not familiar with its potential. The potential for profit is diminished but the plus is that traders are protected from movements in prices. This can be accomplished at a small cost.
This makes it a desirable strategy for traders. Risk reversal can be practiced on a directional call. When a trader instinct senses a bearish or bullish position, he may look for better leverage.
When To Use A Risk Reversal
The risk reversal can guard a trader from a rising stock price. When he is shorting an asset. Investors that are concerned about the price of the stock of a short position can start trading higher.
They can purchase an upside call and then pay for it by selling a downside put. The trade needs to be realized on a one-to-one basis. If the stock rises, the investor would be defended by the upside long call option. But when the stock goes lower. The broker will have to purchase the stock at the short put price point.
It can be implemented as a self-asserting bull trade. The investor is purchasing a rising strike price call option and backing the premium paid. He does this by selling an out-of-the-money put option. The trader is creating a bull trade without any expense. If the investor is right.
This can be confirmed by the stock trading higher. The short put loses value. And the long call will multiply in value. But if the trader has made a wrong forecast about the stock movement. He will be compelled to acquire the stock at the short put strike price. This is risky and can create losses. Because he will have to buy the stock at a lower price in compresence when the investor started the risk reversal. This is a better option than just buying the stock from the beginning.
Risk Reversal Strategy And Underlying Asset
There are several situations in which a risk reversal strategy can bring benefits. When you are bullish on a stock and want to influence your position. In this case, you can write an out-of-the-money put and use the interrelated premium to purchase an out-of-the-money call. This will double down on your bullish view.
The other scenario is in the lead up to events like a stock split, where there is some downside support and the final effect will be large price gains. The last scenario is when a blue-chip asset has a sharp fall in a solid bull market and is not expected to stay at that level over a long period.
Risk reversal strategy can be effective if the stock rebounds in the medium term. Whenever you have a short or long position and want protection, you can use a risk reversal strategy to hedge the position.
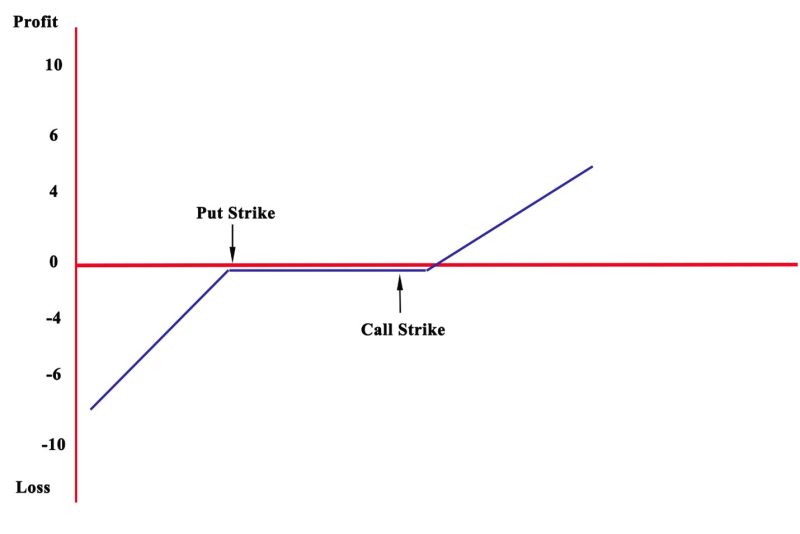
Risk Reversal And Strike Price
If a stock is trading at $50 and is anticipated to rise in the following year. An investor can purchase a 100-strike price call and sell a 70-strike price put for the following price:
- Buy 1 stock 100-strike price call for $5.00
- Sell 1 stock 50-strike price put for $$4.00
- Premium is $1.00 credit
If at expiration the stock trades up to $55. The trader will not make any profit. Because the asset has not attained the strike prices. The upside is that the investor gets a $1.00 credit on the risk reversal. Because of this, he will make a profit of $1.00. If the stock rises up to $110 at expiration. The investor will make a $10.00 profit on the call. Because the stock has gone over the 100-strike price by $10. The risk reversal credit of $1.00 will give the trader a gain of $11.00.
When the stock goes down to $80 at expiration. The trader will get an 80-strike price put. He will have to buy the stock for $80. This results in a $10.00 loss on the put. The risk reversal of $1.00 means a net loss of $9.00.
Application In Stock Price
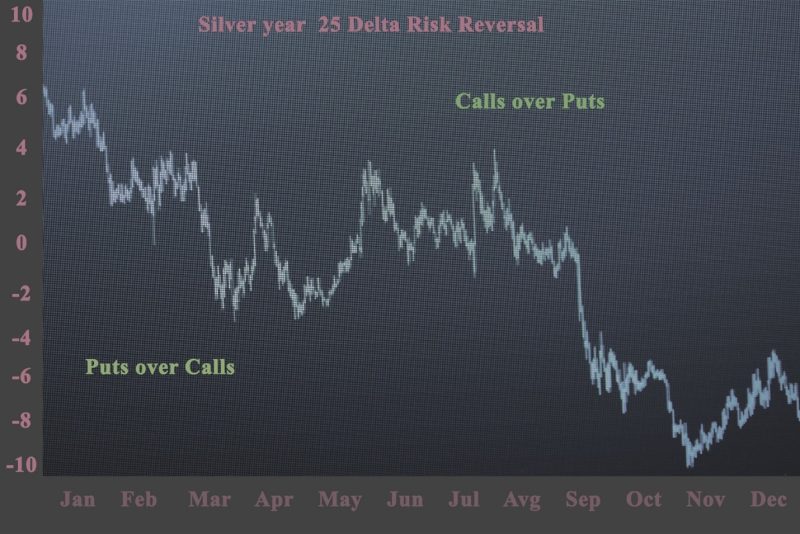
Risk reversals are frequently used to depict the suggested trading prejudice among traders in currencies. It indicates the contrast in suggested volatility between comparable call and put options.
The important thing about risk reversals is if the value is positive or negative. The positive risk reversal means that call options are more costly than put options. The traders that short the currency have weak protection. A negative risk reversal is when put options are more costly than call options. The downside safeguard is also expensive for investors that long the currency.
Maximum Gain vs Maximum Loss
Because a price of a stock can go without limit, the same can be applicable for risk reversal. With the strategy, you can have appreciable price gains when opening a stock position.
But you should keep in mind that the price can go to zero. In this case, the put seller will get assigned stock at the strike price of the put. The maximum loss is equivalent to the put strike and the premium paid when the transaction was started.
Risk Of Early Assignment
The early assignment is always a possible risk when having a short option position in an individual stock or ETF. You can limit the risk by trading Index options.
Usually, early assignments happen on call options when dividend payment is expected. Investors will use the call to take ownership of the share and get the dividend.
Short puts can also be assigned early. The thing to focus on is that early assignment occurs when a short option is in the money. If the underlying asset used in the strategy goes below the short put, brokers need to be assigned on the put which would require them to purchase 100 shares of the underlying stock.
How To Trade A Risk Reversal Strategy?
Synchronized selling of call or put option, and buying the opposite is the usual way to deploy a risk reversal strategy. Both put and call have an identical expiration date.
You may sell an out-of-the-money put option and at the same time purchase an out-of-the-money call option. You will receive a premium which you can then use to buy the call.
Traders will have a net debit if the expense of purchasing the call is higher than the premium you get for selling the put. If an investor makes the opposite trade, he will generate a net credit. When using a risk reversal strategy, a trader is inverting the volatility skew risk. Take into account that out-of-the-money puts are more costly than out-of-the-money calls.
This is because there is demand for puts, that are used as a hedge for long positions. A trader usually sells options with volatility and buys options with lower volatility when making a risk reversal strategy. They are reversing volatility skew risk.
Risk Management For Maximum Profit
The risk reversal has profit potential if realized properly, but it can bring losses if done wrong. This is not a strategy for a beginner. A substantial risk can result from unfavorable price movements when the trade goes the other way than what the investor planed. It is a profitable tactic for veteran investors. They have experience with risk management when doing options trading. This trade has limited sensitivity to variations in intended volatility because it is short one option and long another.
Conclusion
The advantages of the strategy are that it can be used at little expense. It offers traders an opportune risk to reward ratio. The strategy can be used to double down on a bullish risk reversal bet or hedge a position. Risk reversal benefits from the volatility skew that happens in the market.
Out-of-the-money puts trade have larger volatility than the out-of-the-money calls. Because you sell puts and buy a call, it is beneficial because you are selling high volatility and buying cheap volatility. The trade results in a net credit. The reason calls are cheaper than the puts. The disadvantage is that bigger losses can result if the short leg has high margin requirements and using a risk reversal to double down on a position. The strategy is usually used Forex markets as an options tactic that integrates simultaneously buying puts with the sale of calls. The options will have analogous deltas and the same expiration date.
Also Read: The Best Forex Trading Tips
FAQs
Why is it called a risk reversal?
It is called risk reversal because it reverses the “volatility skew” risk that opposes the options trader.
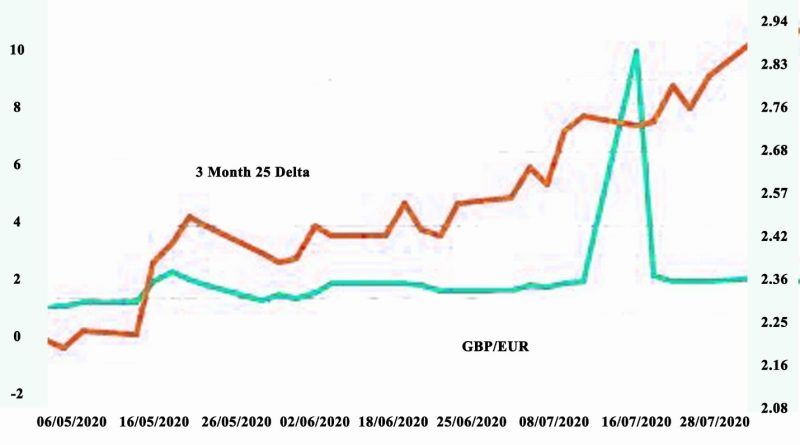
What is a 25-delta risk reversal?
The 25-delta put is the put whose strike has been chosen such that the delta is -25%.
What is risk reversal in sales?
Risk Reversal transfers some risk in a transaction from the buyer to the seller. The seller agrees to make things right in advance if the purchaser doesn’t end up satisfied.
What is a call spread risk reversal?
A call spread risk reversal restores the long call with a long call vertical spread. This creates a defined quantity of possible profit if the underlying asset was to rally. The downside risk is limited by the fact that the underlying stock cannot go below zero cost.



