In the broad tapestry of financial markets, the MOVE Index has emerged as a critical tool for investors to measure volatility in the bond market. As a gauge of implied volatility, the MOVE Index serves as a useful proxy for the uncertainty that pervades the bond market, similar in many ways to how the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) operates within the equity market. It is a sign of the times, an arrow that points to the movement and direction of market sentiment. This article will serve as your helpful guide to understanding the MOVE Index, explaining its relevance and the role it plays in the broader financial ecosystem.
How is the MOVE Index Calculated?
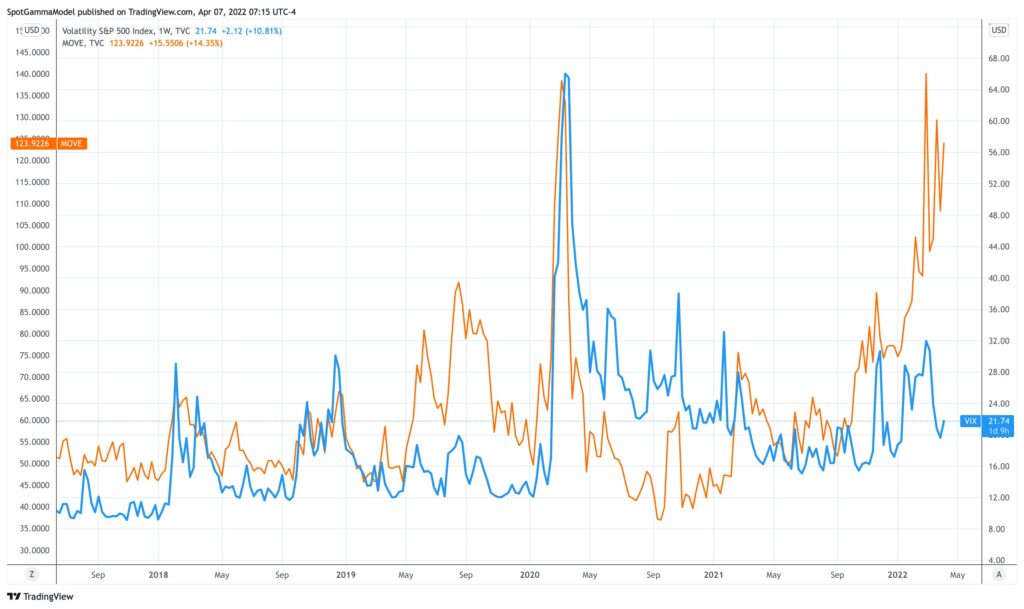
The MOVE Index, provided by the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), is calculated based on the implied volatility of one-month Treasury options. It is akin to the VIX index for the bond market, though they assess volatility in different financial markets. The index is derived from option volatility estimates, more specifically, the Merrill Lynch Option Volatility Estimate, where it gets its name. The measure is taken from U.S. Treasury futures markets and provides an overall level of volatility expected over the next 30 days.
A higher reading on the chart shows a higher expectation of significant price movement, or volatility, while a lower reading indicates a more tranquil market. By clicking on the relevant section of the ICE's website, you can find a free, interactive chart that illustrates the changes in the MOVE Index over time.
Also Read: What are the Best Bond Funds?
MOVE Index vs. VIX Index: A Comparison
When it comes to understanding the ebbs and flows of the financial markets, the MOVE Index and the VIX Index serve as complementary tools. The VIX, often referred to as the “fear gauge“, is focused on the equity markets, reflecting the market's expectation of 30-day forward-looking volatility. It is calculated from the prices of S&P 500 index options.
In contrast, the MOVE Index is the bond market's equivalent, reflecting implied volatility in the Treasury market. A comparison of the two can provide insights into the relative volatility of stocks and bonds. In periods of high volatility, investors often turn to the safety of bonds, which can cause the equity markets to fall and the bond market to rise. Similarly, in periods of low volatility, the equity market often outperforms the bond market.
What Does a Spike in the MOVE Index Mean?
Just like the VIX in the equity market, a spike in the MOVE Index is generally viewed as a sign of increased risk and uncertainty. An abrupt increase in the MOVE Index means that market participants expect significant movement in interest rates. For bond traders and investors, such spikes are a time of caution and reevaluation. It might be an opportunity to hedge their bets or to find new investment opportunities.
Interpreting the MOVE Index
The MOVE Index is more than a measure of bond market volatility. It is also a barometer of market sentiment and a leading indicator of potential changes in monetary policy. For instance, an upward trend in the MOVE Index might suggest investors are anticipating changes in interest rates.
With the bond market being a more direct reflection of economic and policy decisions, the MOVE Index can be a key tool for traders and investors to manage the potential risk and volatility in their portfolios. For bond investors, the MOVE Index is a helpful guide to managing uncertainty, providing insights into the anticipated level of fluctuation in the bond market.
Understanding the Dynamics

The beauty of the MOVE Index lies in its simplicity: it is essentially a standard deviation measure, providing a sense of the range within which bond yields are expected to move. It represents the implied volatility embedded in the option prices of Treasury bonds – basically the expected future volatility of these bonds.
A unique feature of the MOVE Index is its sensitivity to large swings in either direction of the market. That's because the index is an ‘average' of the implied volatility of ‘straddles', an options trading strategy that involves buying (or selling) a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiry date. Therefore, it captures volatility irrespective of whether rates go up or down, allowing it to be an effective tool to gauge uncertainty in the bond market.
Importance of the MOVE Index in Today's Market
In the past few years, the correlation between the MOVE Index and equity markets has strengthened, meaning that spikes in the MOVE Index often coincide with equity market sell-offs. For example, during the financial crisis of 2008, the MOVE Index reached an all-time high, reflecting the heightened uncertainty in the bond market as investors fled to safer assets like bonds.
In today's low interest-rate environment, where central banks worldwide are employing accommodative monetary policies, tracking the MOVE Index has become increasingly important. A sudden rise in the MOVE Index could indicate a sharp increase in bond yields, which could hurt equity valuations, given that higher interest rates generally lead to higher discount rates used to value stocks.
Impact on Forex Trading
The MOVE Index also has implications for the Forex market. Forex traders often look at the bond market for cues about currency direction. An increase in bond yields often attracts foreign investors looking for higher returns, thereby increasing demand for the currency. Therefore, a rising MOVE Index, indicating higher expected volatility in bond yields, could potentially signify future volatility in currency exchange rates.
Also Read: How Does Mark-to-Market Affect Forex Trading?
Bond Market Volatility and Investment Strategies

Understanding the MOVE Index can help investors make more informed decisions. For instance, when the MOVE Index is low, it indicates that the bond market is calm, with little expectation of large price swings. This could present opportunities for bond investors, as bonds are generally considered a safe haven asset class. On the other hand, a high MOVE Index signals potential volatility in the bond market, prompting investors to adjust their portfolios accordingly.
Furthermore, the MOVE Index can serve as a hedge against market volatility. When the index is high, investors might consider buying Treasury options to protect their portfolio from large swings in interest rates. When the index is low, it could be a sign to sell options or invest in other assets with potentially higher returns.
The Relationship Between the MOVE Index and Interest Rates
The bond market's sensitivity to interest rate changes is one of its defining characteristics. When interest rates rise, bond prices fall, and when rates fall, bond prices rise. This inverse relationship is key to the workings of the bond market, and it's also where the MOVE Index becomes particularly valuable. By serving as a measure of implied volatility, the MOVE Index can give investors a glimpse into future interest rate changes.
A spike in the MOVE Index often precedes a period of interest rate volatility. This relationship underscores the importance of the MOVE Index as a leading indicator for potential rate changes. It allows investors to prepare for any adverse market scenarios by adjusting their investment strategies, hedging against risk, or seeking out new opportunities.
The MOVE Index and Other Financial Markets

The MOVE Index doesn't exist in a vacuum. Its movements can also impact other financial markets, such as the equity and Forex markets. For instance, a sudden spike in the MOVE Index could trigger a sell-off in the equity market, as investors flock to the relative safety of bonds. This flight to safety can push up bond prices and cause yields to fall, leading to a dip in the equity market.
In the Forex market, higher volatility in bond yields, as indicated by a rising MOVE Index, could lead to fluctuations in currency exchange rates. If the expected return on bonds in a particular currency increases, foreign investors might buy more of that currency to invest in those bonds, pushing up its value.
Conclusion
The MOVE Index, much like its equity counterpart the VIX, serves as a valuable guide for traders and investors alike, giving them a sense of the prevailing winds in the financial markets. While the index is just one of many tools used to gauge market sentiment, its importance cannot be overstated, given the significant role that interest rates play in our economy.
Investors would do well to remember that the financial markets are inherently unpredictable. Indices like the MOVE and VIX can help shed light on market dynamics, but they are not foolproof predictors of future movements. They are just one piece of the puzzle that traders need to consider as they navigate the often-choppy waters of the financial markets. As always, the best investment strategy is a well-researched and balanced portfolio tailored to your individual financial goals.
Also Read: How to Build a Bond Ladder That Produces Profits
FAQs
I am new to investing, how can the MOVE Index help me make better investment decisions?
The MOVE Index serves as an indicator of expected volatility in the bond market. If you're invested in bonds or are considering doing so, the MOVE Index can give you a sense of the level of risk or uncertainty in the market. For instance, a rising MOVE Index indicates increasing volatility, suggesting a potential increase in risk. This could signal a time for caution. Conversely, a falling MOVE Index suggests a period of calm, which could be a favorable time to enter the market. However, always remember that financial indicators should not be the sole basis for your investment decisions. It's important to consider other factors, do your own research, and consult with a financial advisor if needed.
How is the MOVE Index different from the VIX Index?
While both the MOVE and VIX indices measure market volatility, they do so for different markets. The VIX Index, often referred to as the ‘fear gauge', measures expected volatility in the equity market, specifically for the S&P 500 index. On the other hand, the MOVE Index measures expected volatility in the bond market, particularly in U.S. Treasury bonds. Both indices serve as useful tools for gauging market sentiment and can provide investors with valuable insights into expected market volatility.
Can the MOVE Index predict future changes in the bond market?
The MOVE Index measures the market's expectations of future volatility based on current information. While it provides insights into market sentiment and expected fluctuations in U.S. Treasury bonds, it's not a foolproof predictor of future market movements. Like all indicators, it should be used as part of a broader toolkit and in conjunction with other factors when making investment decisions. It's always important to consider multiple factors, do your research, and if necessary, seek advice from a financial advisor.