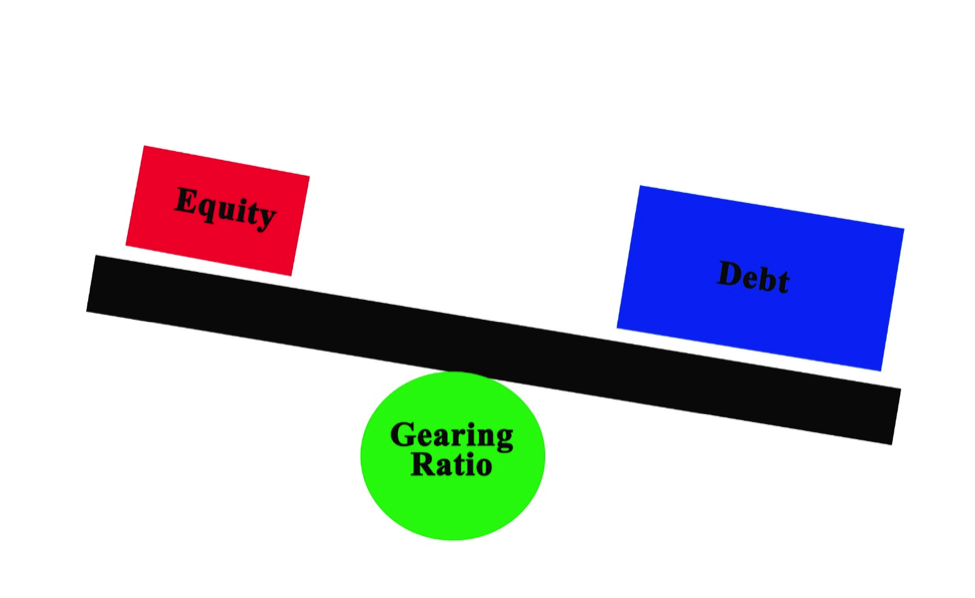
- What Is Gearing Ratio
- Company's Gearing Ratio
- What is a Good or Bad Gearing Ratio?
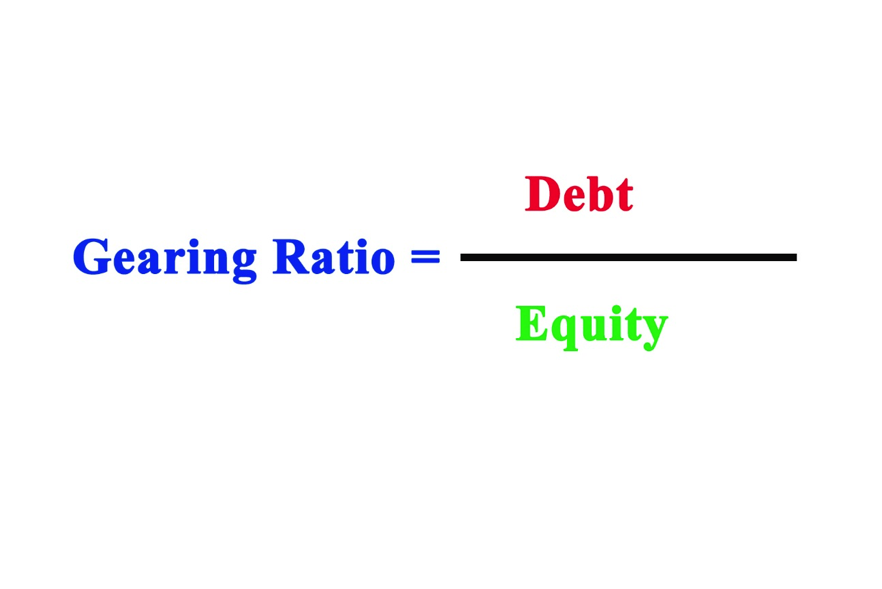
- How Do You Calculate a Gearing Ratio?
- Example of Gearing Ratio
- High Gearing Ratio
- The Benefits of Gearing Ratios
- Disadvantages of Gearing Ratios
- Debt To Equity Ratio
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Gearing Ratio
Investors when to know how a corporation is doing on the books. Marketing usually is one-sided and not to be trusted. Companies in the same industry may have a different industry average. Most investors ask themselves if a company debt is a potential financial risk for them
What are the interest rates, the business's assets, and the chosen capital structure? That’s why brokers use instruments to measure the financial situation in a company.
The gearing ratio compares the debt to capital and total equity in company structures. How it is doing compared to other companies. Gearing ratio calculations make it easy to make decisions about potential investments.
Also Read: Risk Reward Ratio
This is done by comparing the capital a company owns concerning the debt it has accumulated or is using to finance its operations. Analysts use these types of ratios to measure how a company is structured and the risk involved.
Debt service ratios and company assets are calculated differently. Calculating the gearing ratio enables investors to make good decisions.
Company's Gearing Ratio
Investors use gearing ratios to decide if they should invest in a business. The higher the ratio is the more financial risk is present. No rule says that a certain degree of gearing ratio can signal that a company is performing well or badly.
What is a Good or Bad Gearing Ratio?
It is relative to compare well versus bad ratios. Some guidelines can be helpful in locating wanted and unwanted ratios. Everything that is 25% to 50% is the optimal gearing ratio. While everything that is over 50% is a high gearing ratio. Finally, everything under 25% is a low gearing ratio.
Corporations that have a high gearing ratio will finance their operational costs with credits. But this means that there is a larger risk in times of financial turbulence in the economy, resulting in a potential bankruptcy.
How Do You Calculate a Gearing Ratio?
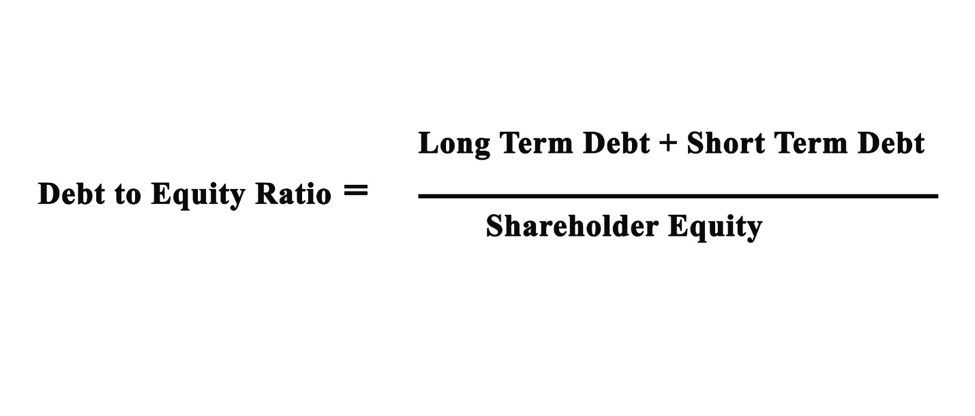
There are dissimilar types of gearing ratios. The most common is the debt-to-equity ratio. It is calculated by adding up the long-term and short-term debt and then dividing it by the shareholder equity.
Example of Gearing Ratio
If a firm is in debt by $4 billion but at the moment it has $2 billion in equity. In this case, the gearing ratio will be 100%. In other words, for every $2 of equity owned by the shareholders, the firm has a debt of $4. This is gearing ratio is considered high.
High Gearing Ratio
The higher gearing ratio signals a high percentage of leverage. But you should know that it does not mean that it is a signal that a corporation is in a bad financial situation. Companies with a high gearing ratio may have a more turbulent financing structure, in comparison with a lower gearing ratio company.
In the case of regulated entities, they usually have higher gearing ratios because they function with larger levels of debt. While monopolistic companies operate with higher gearing ratios, their market position enables them to function with a small risk of default.
Businesses that use costly assets have higher gearing ratios. They refinance their debt with these fixed assets. Companies with a low gearing ratio have more traditional spending habits and try to keep their debts down.
Corporations that have low gearing ratios usually manage these by using shareholders’ equity to finance expenses.
Also Read: Power Hour Stocks
The Benefits of Gearing Ratios
Banks are in the business of offering credit, but there are other institutions that enable companies to acquire debt. The use gearing ratio as an indicator of risk.
If a company is in more debt, that signals a risk of financial turbulence. With gearing ratios, firms can manage their debt. It can make assessments about cash income in the future.
Disadvantages of Gearing Ratios
There are limitations on how much a company’s gearing ratio can measure the financial structure of a company. The gearing ratio mirrors an unsafe financial structure. But this should not be understood as a necessary low-performing financial situation.
Numbers offer perspective into the financial situation of a company. It’s a factor to use it and compare it against past ratios and the competitions ratios.
Gearing ratio analysis can bring advantages to a firm's financial planning when over time. Still, they are a one-time calculation, and may not provide any real meaning.
It is crucial to remember that high gearing ratio can cause high financial leverage. These does not automatically indicates that a company is in financial trouble. Firms with higher gearing ratios usually have more risk. While entities like utility companies commonly operate with higher debt levels.
Debt to Equity Ratio
Investors don't like financial instability; they need to know the capital structure and total assets on the balance sheet. There are numerous ways a company can control its gearing ratio. This is usually done by profit, debt, and expense management.
Debt management: Perhaps the most obvious is debt management. If a company manages its debt efficiently, it should be able to reduce its gearing ratio.
Companies can take steps to pay off their debt and incur less interest long-term. Firms can also utilize debt management schemes to avoid taking out more loans. Firms should attempt to renegotiate debt terms in a bid to reduce long-term liabilities.
Reducing expenses: Expense reduction will decrease liabilities and therefore improve the gearing ratio. Reducing expenses can include anything from renegotiating loan terms, increasing business efficiency, and introducing basic cost controls.
Increasing profits: Increasing profits will help to increase stock price and thus, shareholder equity. Conversely, sometimes taking out loans, in this case, can help a business become more profitable in the long term.
Conclusion
Calculating gearing ratio is a useful indicator of the company’s financial leverage in economic downturns. Many corporations use debt financing to function, but long-term debt can be harmful to companies' potential to develop.
Financial metrics can measure the risk a company's debt can bring to potential investors. Calculating the gearing ratio is not hard if you follow the basic guidelines. Gearing ratio formulas can give insight into companies' financial obligations and interest payments. Highly geared companies have a high amount of debt compared to capital.
Comparing gearing ratios can increase profits and help navigate financial difficulties. Investors need to know the future cash flows and equity capital that a company has at its disposal. Creditor funds and extend credit can indicate if there is a very low risk in the firm's operations.
Some limitations can present from making a good decision, but they can be an instrument of making good investments.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the gearing ratio formula?
The gearing ratio is calculated by dividing total debt by shareholders' equity. It can also be calculated by dividing total debt by total capital.
2. What is a good gearing ratio?
A gearing ratio between 25% and 50% is considered normal for well-established companies.
3. What are examples of gearing ratios?
Common examples of gearing ratios are the time interest earned ratio, the debt-to-equity ratio, debt ratio, and the equity ratio, capitalization ratio.
4. Is gearing ratio and debt ratio the same?
No, the gearing ratio is the broad category, and debt/equity is one of the measures of gearing of the company.